Usage of waste
derived resources
Reduction in specific water consumption in cement operations
Total green energy consumed
We are constantly incorporating best practices to achieve our sustainability goals and targets.
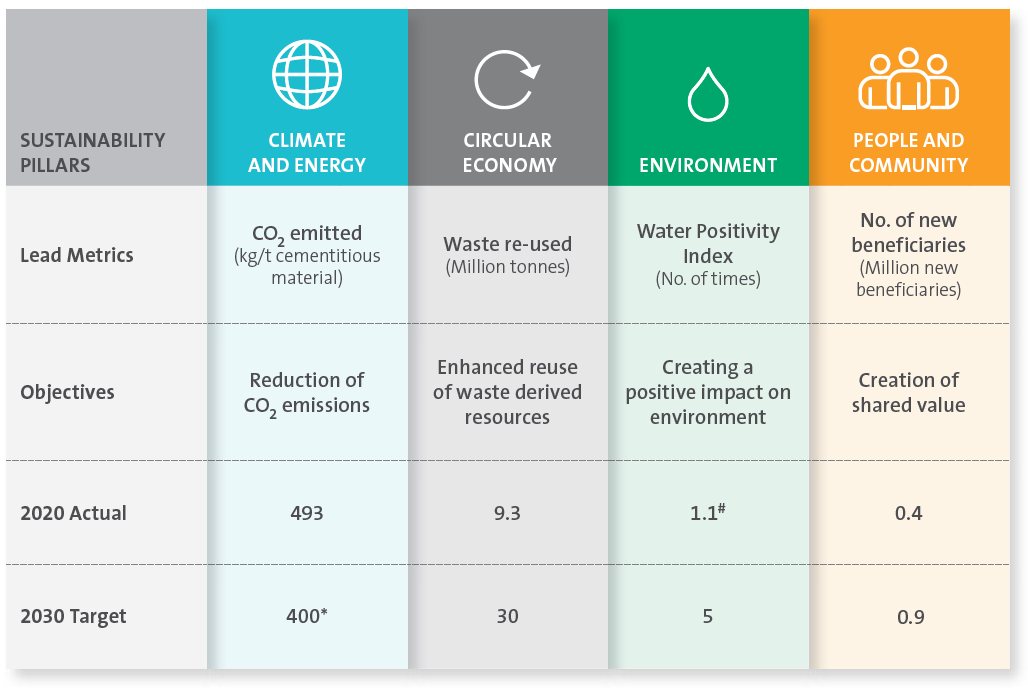
Our SD 2030 Plan focuses on four priority areas, namely Climate and Energy, Circular Economy, Environment, and People and Community. Of these, we have earmarked Climate and Energy, Circular Economy and Environment for action aimed at preservation of natural capital and minimisation of negative impact on the same.
Climate change is among the most pressing issues facing humanity, with all nations being urged to meet the goals of UN SDG 13 Climate Action. As a leading building materials company, we are committed to meeting the rising demands for sustainable cities, while conforming to a low-carbon circular economy. While ACC has already committed to the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi), we are also gearing up to follow in the footsteps of our parent LafargeHolcim, which has signed the net-zero pledge with SBTi.
ACC’s SD 2030 Plan, aligning with
that of LafargeHolcim, has adopted ambitious targets for reduction of specific CO2 emissions to
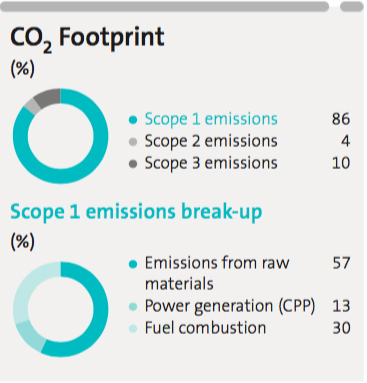
400 kg/t of cementitious material*. We reduced our specific CO2 emissions to 493 kg/t of cementitious material in 2020, from 512 kg/t of cementitious material
in 2019.
We continued to reduce average clinker factor across the full range of our cement portfolio. During the year, we increased the blended cement portfolio from 89% to 90%. All these initiatives helped in significant reduction of average clinker factor by 1.37%.
Reduction of average clinker
factor in 2020
We continue to reduce our thermal energy consumption through a range of ongoing conservation projects, process optimisations and by improving Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR). During the year, we reduced our thermal energy consumption to 742 kcal/kg of clinker from 748 kcal/kg of clinker in 2019. This was despite the disruption across manufacturing processes due to the pandemic.
With an objective to further enhance our renewable energy portfolio, we have installed two solar power plants comprising 5.35 MWp solar photovoltaic plant at Jamul Cement Works, Chhattisgarh and 380 kWp at Kymore, Madhya Pradesh. These two plants have together generated 2.37 Million units in 2020. Thus, we continued to increase our consumption of green energy during 2020, touching 85.27 Million units in all.
Power generated from waste heat recovery decreased by ~14% due to reduced operation of kilns owing to COVID-19. There was a marginal increase in specific electrical energy because of the fluctuations in operations during the pandemic.
STRATEGIC FOCUS AREAS
MATERIAL ISSUES ADDRESSED
SDGs IMPACTED

*Note: From 2020, we have been reporting the specific CO2 emissions in kg/t of cementitious material (instead of kg/t of cement).
Producing lower-carbon cement and concrete is not only about using new technologies; it is also about making proven technologies more effective. We are working to enhance the reuse of waste materials from other sectors to increase our contribution to circular economy.
Around 90% of our product portfolio comprises blended cements (PPC, PSC and Composite cements) which use fly ash and slag to replace clinker. Also, we have modified the process of manufacturing PPC by using wet fly ash (pond ash), which is usually dumped and remains unutilised.
During the year, we consumed 5.33 MT of fly ash and 2.82 MT of slag, 0.4 MT synthetic gypsum, including phosphogypsum and 0.57 MT of alternative fuels and raw materials in cement manufacturing. Additionally, 0.16 MT of waste derived resources comprising fly ash, slag and so on were consumed in concrete production.
While our industry does not generate any process-related waste, there are ancillary activities like maintenance, housekeeping and so on, which generate waste materials like oil-soaked cotton waste, steel scrap, used oil, used filter bags, electrical waste such as used bulbs, batteries and others. We mostly adopt a 3R (Reduce, Reuse and Recycle) approach for managing our waste, wherever practically possible.
We are dedicated to complying with all regulations concerning the safe and responsible management of waste materials. Waste, including waste oil and grease, electrical, electronic waste and steel scrap, is sold to the authorised recyclers. For hazardous waste, the relevant returns are filed with the respective regulatory authorities from time to time.
Waste-derived resources consumed in 2020
(as compared to 9.90 MT* in 2019)
We use advanced technology to provide eco-friendly solutions for waste management, which also helps in substituting traditional raw materials and fossil fuels.
Kerala is well-known for its natural
beauty, spices, wildlife and scenic
landscapes, making it a major tourist
destination in India. However, with
significant increase in industrial
and commercial centres, there has
been a noteworthy rise in plastic
waste,
e-waste, construction sector
waste and household waste. The
Government of Kerala launched the
Haritha Keralam (Green Kerala), an
umbrella mission to integrate waste
management, organic farming, and
water resources management.
Using the first-of-its-kind ‘Geocycle Bubble Barrier’ concept, Geocycle India launched the ‘Plastic Free Agra’ Mission in Agra city, Uttar Pradesh.
Read More*Note: Last year, the reported figure was 12.47 MT which included Crushed Rock Fines but this year onwards it is excluded.
Reduction in specific water consumption
(from 165 litre/t of cementitious material in 2019 to 151 litre/t of cementitious material in 2020)
Freshwater is critical for sustaining healthy communities and natural ecosystems. During the year, we continued our efforts to conserve water and improve our water harvesting capacities. We comply with stringent environmental regulations to ensure that our activities, in particular raw material quarrying, do not endanger local water bodies and groundwater. During the year, various efforts were made for strengthening water conservation and harvesting to closely monitor water consumption augmenting water harvesting structures in communities and optimising processes.
While specific freshwater consumption in cement operations remained almost the same as in 2019 with 77.8 litre/t of cementitious material, we consumed ~1.75 Million m3 of harvested rainwater in our cement operations, which is ~50% of the total water consumption.
Jamul Cement Works decided to develop rainwater harvesting structures in nearby village schools to help conserve water to solve acute water crisis faced by the community. While it rains heavily in the area during the monsoon, the communities are unable to store the runoff water. Also, school premises witness heavy waterlogging during monsoons. Thus, a solution was devised to help address both the issues at once.
The plant installed three rainwater harvesting structures at Government Primary School, Pathariya and Government Primary School Nandini Khundini, which solved the problem. This initiative conveyed an important message to the students and community members about the conservation of a precious resource in a cost-effective manner.
During the year, we continued our efforts to conserve nature and preserve biodiversity. Our initiatives focused on the conservation of particular floral/faunal group at some plant locations under the ‘B-Buzz’ project. As part of the B-Buzz programme, while one unit worked towards improving avian biodiversity by creating a fruit garden, two units developed a herbal garden – ‘Aushadi Udyan’ at their locations. Some of our sites have also initiated their ‘B-Buzz’ with a Butterfly Garden within their own premises.


During the year, we continued our efforts to conserve nature and preserve biodiversity. Our initiatives focused on the conservation of particular floral/faunal group at some plant locations under the ‘B-Buzz’ project. As part of the B-Buzz programme, while one unit worked towards improving avian biodiversity by creating a fruit garden, two units developed a herbal garden – ‘Aushadi Udyan’ at their locations. Some of our sites have also initiated their ‘B-Buzz’ with a Butterfly Garden within their own premises.
‘Van Upvan’ is an initiative under the B-Buzz programme, which focuses on creating a forest by adopting Miyawaki methodology. This is a Japanese afforestation technique that helps plants grow 10 times faster and ensures that the resulting plantation is 30 times denser than usual. In 2020, Chanda Cement Works tried Miyawaki plantation method in a small area of 300 sq m on a trial basis. Steps followed in this process included:
Read MoreDuring the year, we set up 43 new GBCs totalling 187 by the end of December 2020. GBCs have collectively helped utilise 70,740 tonnes of fly ash, conservation of 1,53,271 tonnes of the Earth’s natural topsoil and avoidance of 10,788 MT of CO2 emission during the year.
Low cost housing projects
facilitated through GBCs

We have a long and successful track record of meeting ambitious targets for reducing CO2 emissions from our activities. We report on our CO2 emissions in line with the Greenhouse Gas Protocol developed by the World Resources Institute and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD).
To control other air emissions, we invest in advanced technologies such as filter systems and ensure regular maintenance of equipment at our manufacturing operations.
Dust emission control: Various maintenance activities were undertaken through in-house and third-party teams for rectification of Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) internals, replacement of damaged bags, etc. These resulted in ensuring stack dust emissions in cement plants was <30mg/Nm3.
NOx emission control: NOx emission compliance was ensured through primary and secondary measures for NOx control and implementation of Systematic Non-Catalytic Reduction (SNCR) systems in integrated cement plants.
SOx emission control: SOx emissions are well within the specified regulatory limits. There is a significant increase in SOx emissions intensity in the year 2020 as compared to 2019. This is due to change in raw material quality and change in fuel at Chanda. Appropriate measures are being taken to keep SOx emission within regulatory limits.
#Not externally verified.
*Note: From 2020, we have been reporting the specific CO2 emissions in kg/t of cementitious material (instead of kg/t of cement).

CDP rating
During the year, we attained CDP – B rating which is the management band, indicating that a company is taking coordinated action on climate issues.