The Indian economy continues to demonstrate resilience amid global headwinds. India’s continued outperformance vis-à-vis major global economies reflects the economy’s structural strength and ability to absorb external shocks, propelled by robust private consumption, increased public investments, and a favourable government policy.
These developments, in turn, bode well for the country’s cement sector, with an expected 11% y-o-y growth in consumption for FY 2023-24. Ambuja Cements maintains its position as a frontrunner in the industry, emphasising focused capacity expansion, more comprehensive market coverage, operational excellence, and a commitment to sustainability.
Indian Cement Industry Snapshot
Cement producer
In the world
Installed
capacity
Per capita cement
consumption

Accelerated Economic Momentum
Currently, India is ranked as the 5th largest economy, with an estimated GDP of USD 3.7 trillion. This achievement was made possible due to substantive and incremental economic and structural reforms, that has helped to make economy more competitive, efficient and resilient.
With an aspiration to emerge as a USD 5 trillion economy, the government has consistently invested in augmenting the country’s infrastructure to support growth. Furthermore, focused interventions to drive the manufacturing sector coupled with an accelerated pace of digitalisation are supporting the country’s all-round growth.
Focused Investments in Infrastructure
Marching towards the vision of Viksit Bharat, the Government of India, in its interim budget for FY 2024-25, has increased infrastructure investments by 11.1% to `11.11 lakhs crore with the majority of the investments earmarked for augmenting road infrastructure (`2.72 lakhs crore) and railways (`2.52 lakhs crore).
Key highlights include:
-
Implementation of three major
economic railway corridor
programmes under the PM Gati
Shakti scheme for enabling
multi-modal connectivity to
improve logistics efficiency and
reduce costs:
− Energy, mineral, and cement corridor
− Port connectivity corridor
− High-traffic density corridor
- Expansion of metro rail and NaMo Bharat in large cities with a focus on transit-oriented development
- Expeditious continuation of existing airports and development of new airports
- Projects relating to port connectivity, tourism infrastructure, and amenities to be taken up on islands including Lakshadweep
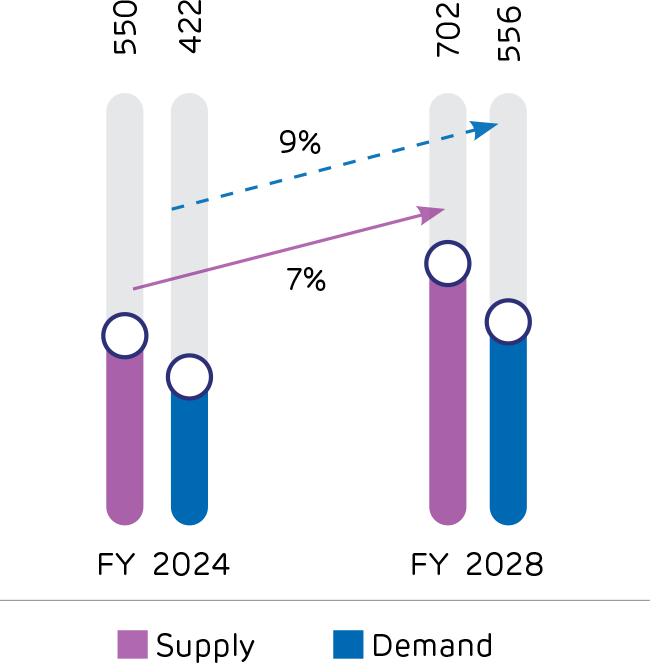
Cement Demand Growth Projections
(Demand to grow faster than supply)
Estimated share of real estate
sector to GDP by FY 2033-34
from ~8 % in the previous year
Source: Confederation of Real Estate
Developers’ Associations of India (CREDAI)
Housing Sector Continues to Grow
The idea of home ownership, especially in the post-COVID-19 scenario, is driving the growth of the housing sector in urban and rural India, which remains the principal consumer of cement in the country. A growing housing sector, which typically accounts for 60% to 65% of India’s cement consumption will continue to remain as the key demand driver in future. In the Union Budget 2024, the Government has allocated `11,11,111 crore for safe housing and other allied infrastructure development. Infrastructure led investments and mass residential projects will continue to keep India’s future cement demand strong.
Leading with Sustainability
The Indian cement industry is ahead of its global peers with consistent strides in its commitment to a net-zero target by 2050. Against the global average of 0.61 tCO2e/t cement, the Indian cement companies have a lower carbon footprint of 0.56 tCO2e/t cement. This lower carbon footprint of Indian cement companies is backed by their higher blending ratios (higher mixing of fly ash and steel slag) that in turn reduces their clinker consumption.
ACC Cements’ positioning
Aligned with the nation’s growth vision, ACC is consistently investing in augmenting growth, organically and inorganically. Furthermore, it invests in digitalisation to drive operational excellence and enhance profitability. Cognisant of the growing importance of the ecological impact of cement, the Company is substantially building capacities in alternative energy generation, reducing finite resource utilisation, and driving the prosperity of communities around the areas of its operations.
Key Growth Drivers
Population
India, with a population of 1.44 billion people, remains one of the most populous countries in the world, driving continuous demand for housing units. Furthermore, the country’s lion’s share of the population falls in the working-age category, boosting the prospects of the real estate industry.
Urbanisation
Between 2022 and 2047, India’s urban population is likely to increase by 328 million, driving the demand for urban dwellings and increased infrastructural developments.
Consumer Spending
GDP per capita in India, is expected to double from below USD 2,500 in 2022 to nearly USD 4,000 by 2028, with almost two in three citizens likely to reach middle-class status within the next 25 years.