
Eco-Consciousness
Sustainability lies at the heart of ACC’s strategy. The Company is advancing decarbonisation through green power investments, increased alternative fuel use, and targeted Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR) goals. A robust Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework enables proactive climate risk assessment, driving innovation and competitiveness. The Company has outlined its goals in its Sustainable Development 2030 (SD 2030) Plan and is making focused efforts to achieve them before planned timelines.
Focus Areas
| Net Zero | Energy Efficiency | Water Positivity | Waste Management & Circular Economy |
Biodiversity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Development and Key Initiatives
|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Performance Indicators
484 kg/tonne
of Cementitious Material Scope 1 Emissions
22 kg/tonne
of Cementitious Material Scope 2 Emissions
18%
Renewable and Green Power |
734 kCal/kg
of Clinker Specific Thermal Energy Consumption
75 kWh/tonne
of Cement Specific Electrical Energy Consumption
10.5%
Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR) |
1.04X
Water Positive
52%
Gross Water Requirement Met through Harvested Rainwater |
0.55 MMT
Waste Co-processed
12 MMT
Waste-derived Resources Used
7.6X
Plastic Negative |
5.1 million
Trees Planted till FY 2024-25
No Net
Deforestation |
Material Topics
- 1 Climate and Energy
- 2 Air Quality
- 3 Water Management
- 4 Circular Economy
- 5 Biodiversity Management
- 6 Sustainable Construction
Stakeholders Impacted
-
 Communities and NGOs
Communities and NGOs
-
 Government and
Regulatory Bodies
Government and
Regulatory Bodies
-
 Suppliers
Suppliers
-
 Channel Partners
Channel Partners
-
 Employees
Employees
SDGs Impacted
Sustainability Strategy
Sustainability principles are embedded across the Company’s value chain and ACC strives to foster sustainable practices across the business. Through the introduction of green products, fossil fuel substitution, increased shared on Green Power and clinker factor optimisation, ACC is determined to progressively reduce its environmental impact. Together with Ambuja Cements Limited, ACC is among the only two Indian cement manufacturers committed to achieving Net Zero by 2050, ahead of India’s commitment to be Net Zero by 2070.

Strong Governance for Sustainability Oversight
- Corporate Responsibility Committee: Oversees sustainability agenda and climate change mitigation
- Independent Directors: Provide guidance on long-term targets.
- Senior Management: Leads execution of sustainability initiatives, aligning with business goals
- Regular Monitoring: Ensures continuous improvement and accountability by management and the Board
Environmental Policy and Management System
ACC’s comprehensive Environmental Management System aligns policies, procedures and practices with industry best standards, enabling proactive management of climate risks, waste reduction and recycling efforts.
The Company actively promotes the integration of climate change measures with national and global policies, demonstrating its commitment to broader environmental initiatives and sustainable practices. Implementation of the policies is overseen by the Corporate Responsibility Committee (CRC), which consists of independent directors and is accountable to the Board.

| Performance Highlights for FY 2024-25 | ||
|---|---|---|

Net Zero
Commitment By 2050 with targets |

484 kg/tonne
of Cementitious
Materials |

22 kg/tonne
of Cementitious
Materials |
18%
Renewable and Green Energy Used |
12 MMT
Waste-derived Resources |
1.04 X
Water Positive |

7.6X
Plastic Negative |

5.1 million
Trees Planted till FY 2024-25 |

94%
Blended Products |
Climate and Energy
Climate Strategy
The Company’s climate initiatives align with national and international frameworks, including the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs). and are focused on reducing the Company’s carbon footprint, building resilience and achieving Net Zero emissions, ACC has conducted a climate risk assessment for all plants based on TCFD and IFRS S2 guidelines. This analysis identified physical and transitional risks, enabling the development of mitigation strategies to address climate change impacts and enhance business resilience.


The assessment has also helped in identifying opportunities and taking initiatives to mainstream the opportunities into business such as the use of renewable energy, setting up of Waste Heat Recovery Systems (WHRS), etc.
Climate Governance
The Board and senior leadership team conduct quarterly reviews to assess progress against the Company's goals and targets. The Corporate Responsibility Committee (CRC), which includes independent directors, oversees sustainability efforts and monitors climate-related KPIs.
Senior management ensures the integration of the Company’s broader sustainability strategy, supported by its ESG team responsible for shaping and implementing the ESG agenda.
The functional teams drive initiatives to reduce carbon footprint, build resilience against climate risks and encash opportunities The Risk Management Committee (RMC) supervises sustainability and ESG risks. Climate-related risks have become integral to the Company’s enterprise risk management process, with performance improvements discussed during CEO and COO plant visits.
Climate Risks and Mitigation Measures
The Company is aware of the climate-related risks it faces, including increasing regulatory pressures, rising energy costs and physical risks such as extreme weather events disrupting production and supply chains. Additionally, the demand for reduced carbon emissions in cement manufacturing is growing. To manage these risks and ensure business continuity, ACC has integrated climate change risks into its comprehensive Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) strategy. ACC considers both, physical risks caused by the increased frequency and severity of climate and weather events, and transitional risks associated with economic, technology or regulatory changes. It has conducted a thorough Climate Change Risk Assessment, covering short, medium and long-term horizons, considering both, physical and transitional risks. These challenges present opportunities for innovation, sustainability leadership and competitive advantage.
Scenario Analysis
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has developed scenarios known as Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSP) to simulate impact of climate change under different scenarios of temperature rise. ACC conducted a climate risk assessment across all its sites, analysing physical risks like flooding, drought, cyclones and wildfires under IPCC scenarios SSP1-2.6, SSP2-4.5 and SSP5-8.5. This evaluation enabled the Company to understand potential impacts and prepare effective strategies to mitigate risks associated with varying greenhouse gas emission pathways.

List of Physical Risks
| Risk Category | Risk Subcategory | Risk Description |
| Acute Physical Risks | Flood Pluvial | Excessive rainfall can result in pluvial flooding, causing substantial damage and operational disruptions. |
| Cyclone | Over the past four decades, the frequency of intense cyclones (Category 3 and above) has steadily increased. If this trend persists with climate change, the heightened wind speeds of these storms could pose severe threats to infrastructure and assets, potentially causing catastrophic damage. | |
| Wildfire | Temperature and precipitation patterns significantly influence conditions that promote wildfires. Rising temperatures make wildfire-prone regions warmer and drier, increasing the likelihood of intense wildfires, which pose serious risks to assets and may result in potential shutdowns. | |
| Chronic Physical Risks | Extreme Temperature | Global warming driven by climate change has resulted in severe consequences. Rising temperatures worldwide have triggered farreaching impacts. |
| Water Stress | Ongoing water scarcity can exacerbate climate change impacts, leading to more frequent and severe droughts, heatwaves and an elevated risk of wildfires. Reduced water availability may also threaten food security, disrupt ecosystems and spark social unrest as competition for this vital resource intensifies. |
List of Transitional Risks
| Risk Category | Risk Subcategory | Risk Description |
| Transition Risks | Policy and Legal | The PAT scheme sets three-year energy-saving targets for energy-intensive industries like cement production, enabling the certification and trading of surplus savings, with financial penalties for non-compliance. Additionally, Renewable Purchase Obligations (RPO) mandate a minimum use of renewable energy and upcoming policies may introduce carbon pricing mechanisms, impacting operations and finances, if targets are not met. |
| Technology | The limited commercial viability of low-carbon technologies like CCUS presents operational risks, as their implementation remains costly and it is still in the developmental phase. Additionally, the evolving regulatory landscape and lack of clear commercial evidence create uncertainty, further complicating their adoption and impacting operations. | |
| Market | Although captive limestone mines ensure secure raw material supply, rising cost of fuels like coal and coke pose financial risks. These fuel price increases are influenced by changing climate conditions, adding to the company's operational vulnerabilities. |
Risk Mitigation
According to the Company's climate risk assessment, none of its sites currently face physical climate risks. However, ACC is implementing site-specific strategies to address potential future scenarios and minimise the impact of unforeseen events on operations. These proactive measures integrate adaptation strategies into existing operations, focusing on short, medium and long-term goals to ensure all future developments are designed to be resilient and sustainable.
Internal Carbon Pricing
ACC has implemented an Internal Carbon Pricing (ICP) mechanism, assigning a value of USD 28 per tonne of CO2, to foster sustainability and climate responsibility. This includes a shadow pricing model that quantifies financial risks at site and organisational levels, helping ACC manage climate-related risks, reduce its carbon footprint and drive low-carbon investments while identifying opportunities for sustainable growth.
Objectives of Implementing Internal Carbon Pricing
- Emission Reduction
- Employee Engagement
- Carbon Planning
- Investment Decisions
- Supplier Selection
- Operational Efficiency
- Regulatory Compliance

Net Zero Commitment
ACC leads climate action and sustainability within its sector, aiming to play a pivotal role in India’s net zero emissions goal. Committed to achieving net zero emissions by 2050, the Company’s 2050 Net Zero targets are already validated by SBTi. ACC is the only large cement manufacturer in the country to have its targets validated by SBTi. The Company also aligns with the Global Cement and Concrete Association (GCCA) Roadmap for Net Zero Concrete by 2070. ACC’s validated SBTi targets can be viewed on the SBTi Target Dashboard.
Emission Reduction Targets 2030
ACC Limited commits to reduce gross Scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions 18.5% per tonne of cementitious material by FY2030 from a FY2023 base year. Within this target, ACC Limited commits to reduce gross scope 1 GHG emissions 16.3% per tonne of cementitious material and gross 2 GHG emissions 53.1% per tonne of cementitious material within the same time frame.
The target boundary includes biogenic land-related emissions and removals from bioenergy feedstocks.
Performance on SBTi Targets
| GHG Emissions | Scope 1 | Scope 2 |
| Target Year 2030 |
421 kg/tonne
Cementitious Material |
10 kg/tonne
Cementitious Material |
| Performance in FY 2024-25 |
484 kg/tonne
Cementitious Material |
22 kg/tonne
Cementitious Material |
ACC to Gain from Ambuja being Signatory to AFID
ACC is expected significantly
benefit from the partnership
between its parent company
- Ambuja Cements Limited
becoming signatory to
the Alliance for Industry
Decarbonisation (AFID), a
global coalition focused on
achieving Net Zero - in line
with the Paris Agreement.
Ambuja is the first cement
manufacturer to join AFID,
facilitating the exchange of
insights between stakeholders
in energy-intensive sectors.
Committed to Net Zero
by 2050, Ambuja has set
Science Based Targets and
plans to invest ` 100 billion in
renewable energy, including
1 GW capacity and
376 MW
from Waste Heat Recovery
Systems (WHRS).
Pioneering Zero-Carbon Heating Technology
The Company is progressing towards its Net Zero ambitions by adopting advanced zero-carbon heating technology to decarbonise its cement manufacturing process. Through a strategic partnership with Finland-based technology and engineering firm Coolbrook, ACC will implement Coolbrook’s groundbreaking RotoDynamic Heater (RDH) technology across its facilities. This innovative solution will drastically reduce the Company’s reliance on fossil fuels while significantly lowering carbon emissions, reinforcing its commitment to sustainable and environmentally responsible operations.

Decarbonisation Levers at ACC Limited Cements
-
Higher Energy Efficiency
-
Increasing consumption of alternate fuels

-
Increase in Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR)

-
Improved Technology

-
Optimising clinker factor
-
Alternate raw materials
-
Zero-carbon heating technology

-
Innovation and optimising the use of natural resources

-
Decarbonisation of Electricity
-
Use of renewable energy

-
Waste Heat Recovery Systems (WHRS) for Power generation
-
No new fossil fuel-based captive power plants

-
Decarbonise Supply Chains
-
Supplier Engagement for reducing carbon footprint

-
Procurement Policy and Choices

-
Increasing rail and sea transport
-
Business Model Innovation
-
Use of Electric Vehicles (EVs)


Future Initiatives
- Pilot on carbon capture and utilisation/storage
- Future-ready technologies like green hydrogen, carbon capture and utilisation

Energy Management
To promote continuous improvement, ACC conducts regular energy audits to identify areas of enhancement and track its progress against set targets. The Company’s operations are ISO 50001 certified, and it offers training programmes to employees to raise awareness on energy efficiency. This includes an in-house course on Energy and Emissions, available through its online platform, E-Vidyalaya-Percipio. com. By focusing on innovation and energy efficiency, the Company aims to reduce thermal and electrical energy consumption and optimise energy costs. With its investments, the Company is on track to achieve its goal of reducing energy consumption by 2030.

Enhancing the Energy Efficiency of Operations

Using Alternative
Fuels
(Co-processing)
Improving Thermal Substitution Rates
Waste Heat Recovery Systems (WHRS)
Renewable Energy
Green Products
Thermal Energy
Total Energy Consumed in FY 2024-25
Energy Consumed from
Renewable and
Green Power
of Cement-specific Electrical
Energy Consumption
Energy Consumption
As a high energy consuming industry, cement manufacturing demands effective energy management to optimise costs and minimise environmental impact. ACC monitors energy performance at all sites and reviews key findings during monthly management meetings and quarterly Board meetings focus on improving energy efficiency, reducing consumption and achieving cost savings. The Company is working towards lowering thermal and electricity usage and taken targets for 2030.
Energy Efficiency
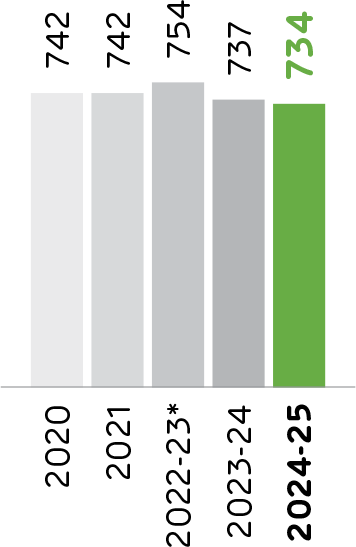
The Company continues to reduce both thermal and electrical energy consumption per tonne of product. Several plants participate in India's Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) scheme, with specific thermal energy consumption steadily decreasing over time. PAT identifies high-energy industries as designated consumers, requiring them to file annual energy consumption returns and conduct mandatory energy audits. The scheme sets energy consumption norms, verifies (Ecert) savings, issues energy savings certificates and facilitates trading of these certificates. It has resulted in the reduction of energy use and carbon emissions, which has contributed to more sustainable operations.
Specific Thermal Energy Consumption
(kcal/kg of Clinker)
Renewable and Green Power
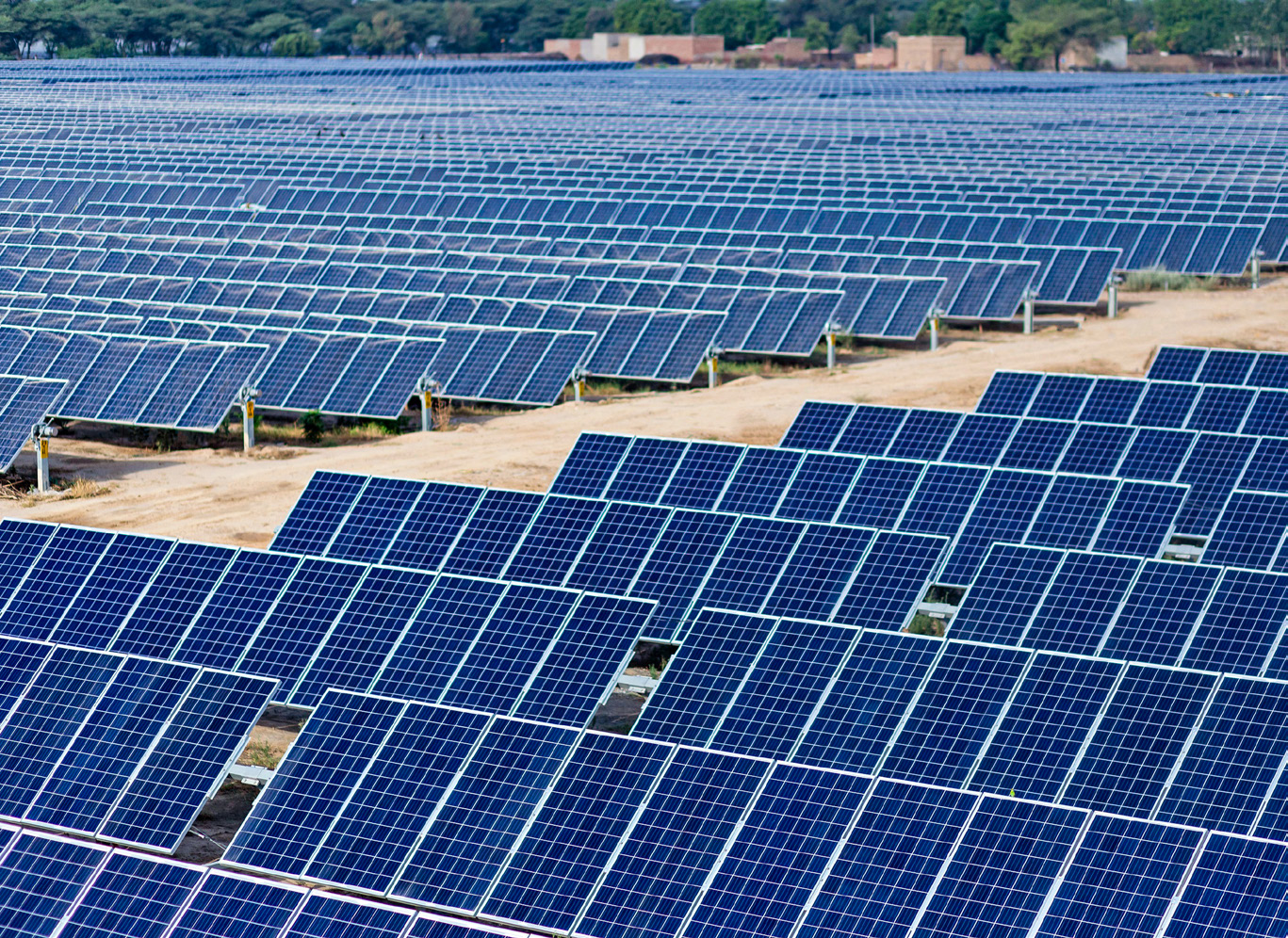
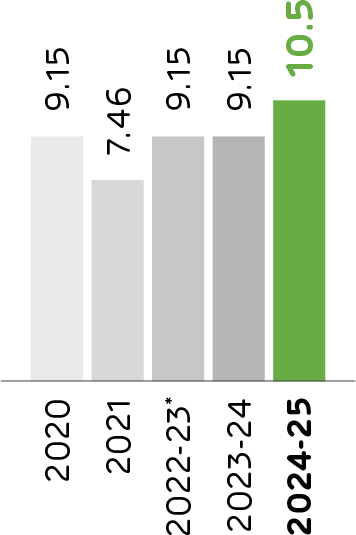
ACC is investing in renewable energy to reduce its carbon footprint and minimise reliance on conventional fossil fuel-based electricity. The Company aims to increase its share of green power to 60% by 2028 through a I 100 billion investment by its parent company – Ambuja Cements Limited, a significant expansion, focusing on solar, wind energy and Waste Heat Recovery Systems (WHRS). This strategy supports ACC's commitment to environmental sustainability, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting the use of clean energy.
Renewable and Green Power
Consumed out of Total Power
Consumption
Alternative Fuel Resource (AFR)
ACC adopts a sustainable approach to managing industrial, agricultural and municipal waste through advanced co-processing technology. The Company operates pre-processing and co-processing facilities across India, each equipped with storage areas, feeding arrangements and laboratories. These state-of-the-art facilities enable efficient waste management, focusing on energy recovery and recycling. In line with its commitment to sustainability, ACC is ramping up investments to modernise and enhance these facilities.
Expert teams provide solutions to like-minded customers, helping increase the utilisation of waste in manufacturing. The pre-processing facilities play a critical role in converting heterogeneous waste into a homogenised mix, reducing reliance on fossil fuel. With continuous upgrades to its waste management infrastructure, ACC consumed 0.55 million tonnes of alternative fuel during the reporting period. The utilisation of these waste materials replaces fossil fuels, preventing them from ending up in landfill sites and causing environmental harm. By adopting alternative fuels, the Company further strengthens its commitment to sustainable and responsible waste management practices.
Alternative Fuels Consumed
Waste Co-processed
(lakhs tonnes)
Pioneering Sustainable Waste Management through Geoclean
ACC's waste management division,
Geoclean, is revolutionising
waste disposal for municipalities
and industries with innovative,
eco-friendly solutions.
By harnessing co-processing
technology, Geoclean enables
resource recovery, reducing
landfill waste and minimising
environmental impact.
With seven pre-processing
and 13
co-processing facilities,
Geoclean increased its Thermal
Substitution Rate (TSR) to
10.5% in FY 2024-25.
Sustainable waste management is crucial for aligning with the Company's broader sustainability and carbon reduction goals. Collaborating with over 20 municipalities and multiple industries, Geoclean diverts waste from landfills, remediating over 10 legacy sites and reclaiming 100+ acres.
In FY 2024-25, Geoclean co-processed over 5.5 lakhs tonnes of waste. Expanding operations, it aims for 28% TSR by FY 2027-28, further strengthening its efforts to abide by circular economy principles and ensure responsible waste management.
The Company is focused on maximising TSR by co-processing industrial and non-industrial waste, including biomass and plastics, in kilns and captive power plants, thereby reducing reliance on conventional fuels such as coal.

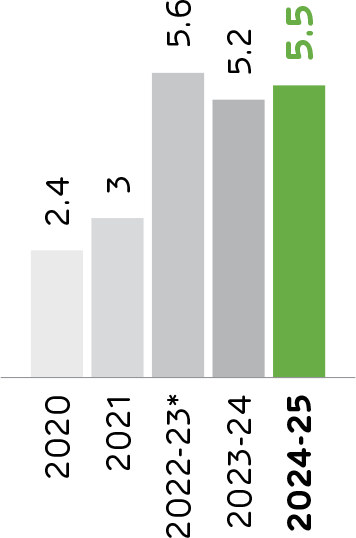
Thermal Substitution Rate
Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR) reflects the percentage of fossil fuels replaced by alternative sources like biomass, industrial waste, and refuse-derived fuel in cement manufacturing. A higher TSR reduces reliance on non-renewable resources, cuts carbon emissions, and drives a circular economy by transforming waste into energy. Across the industry, cement plants are adopting advanced TSR strategies to achieve greater sustainability while maintaining operational excellence.
ACC's thermal substitution rate (TSR) has been steadily increasing over the years, with a target of reaching 28% by 2030.
Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR)
Thermal Substitution Rate
(in %)
Environmentally-friendly Products
ACC is a leader in producing and distributing blended cement, known for its eco-friendly properties and reduced clinker content. By incorporating materials such as slag and fly ash, ACC promotes environmental preservation while enabling the construction of strong, durable infrastructure across India. ACC products are certified by GRIHA, highlighting ACC’s commitment to sustainability and quality in its offerings.
Clinker Factor
Blended Cement's Mix in the Entire Product Mix
ACC has implemented various air pollution control measures, including Electrostatic Precipitators (ESPs) and bag filters for flue and process emissions. Closed conveyor belts have been installed for material transfer and dust suppression methods such as water sprinkling on roads and tyre washing have been deployed. Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS) are in place at all plants to monitor SO2, NOx, particulate matter and other significant emissions, with results displayed digitally across all monitoring locations.
Air Emissions
In addition to greenhouse gas emissions, fuel combustion during operations generates air pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulphur oxides (SOx), exacerbating the environmental impact of the industry. Business activities also contribute to particulate emissions through fuel combustion and vehicular movement.

Water Management
Water, a vital natural resource, is central to ACC’s SD 2030 plan and sustainability efforts. While cement manufacturing employs a dry process, water is judiciously used for cooling, dust suppression and domestic consumption. ACC has achieved a water-positive status and aims to reach 5x by 2030. Recognised internationally by Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) for water security leadership, ACC’s robust water stewardship policy focuses on conserving water resources and supporting both its operations and local communities.
Objectives of Water Stewardship Framework
Reduce Dependency on Freshwater
Seek to minimise reliance on freshwater resources for operations
Ensure Water Security
Ensure water security for communities residing beyond their immediate boundaries
Become Water Positive
Aim to continue being water-positive through sustainable water management practices

Wastewater Discharged
Water Recycled on Net Basis
Gross Freshwater Consumption
from
Harvested Rainwater
Gross Water Positive

Water Withdrawal and Consumption
The Company relies on diverse water resources but prioritises minimising its impact on shared sources. By continually assessing and improving water withdrawal processes, ACC adopts efficient and sustainable water management practices. Proactive measures ensure the responsible and judicious use of water, reinforcing the Company’s commitment to environmental stewardship.
Water Consumption in Production
Operations in Water Stressed Areas
Three of ACC's plants are located in water stressed areas where efficient water management is essential. Despite these challenges, the Company remains fully compliant with regulatory requirements while striving to minimise its impact on local water resources by maximising the use of harvested rainwater and recycled water.
Water Intensity
ACC has set an ambitious goal to reduce freshwater usage intensity per tonne of cement produced. Over the years, the Company has achieved significant improvements in water intensity and is on track to meet its target well ahead of schedule.
Per tonne of cementitious material
Wastewater Recycling and Reuse
Aligned with its commitment to sustainability, the Company has established robust wastewater recycling and reuse practices across its units. These initiatives are designed to enhance water efficiency, reduce dependence on freshwater sources and minimise its overall water footprint. Recycled water is effectively utilised for purposes such as dust suppression and gardening, reflecting the Company’s dedication to responsible water management.
Wastewater Discharge
ACC recycles and treats wastewater generated at its plants for uses such as gardening and dust suppression, ensuring no discharge occurs outside the premises.
Rainwater Harvesting and Conservation
Rainwater harvesting and conservation initiatives inside our boundary and beyond our boundary include utilisation of closed mine pits for rainwater harvesting and groundwater recharge, revival of ponds in rural areas checkdam, roofwater harvesting etc. Partnerships with government bodies for projects like check dams, engagement with developers for rainwater harvesting, implementation of modular zero-water curing solutions, and deployment of rainwater harvesting projects across communities ensure water security for our operation and communities.
Waste Management and Circular Economy
ACC is committed to sustainable resource use, waste reduction and circular economy principles. The Company exceeds regulatory standards and adopts industry best practices to minimise environmental impacts. By complying with relevant environmental laws, ACC ensures responsible waste management across its operations.
Waste Generation
Waste minimisation and
recycling form an integral
part of ACC’s sustainability
strategy. Regular waste audits
are conducted to identify
improvement opportunities and
implement action plans for waste
reduction. ACC has consistently
minimised waste generation
and as part of its sustainability
commitment, sends zero hazardous
waste to landfills and conducts
regular employee awareness
training sessions to promote
responsible waste management
practices and create a culture of
environmental stewardship.
Following types of waste are
generated by ACC:
- Plastic waste
- E-waste
- Bio-medical waste
- Construction and Demolition waste
- Battery waste
- Other hazardous waste
- Non-hazardous waste
Total Waste Generated
For more details of waste generation, please refer to BRSR, Principle 6, Question 9.
Waste Management
ACC strives to achieve waste collection and segregation at source, classifying materials as hazardous or non-hazardous and storing them in designated areas. Each waste is managed as per the regulatory requirements of that waste and as per the condition stated in consent to operate. The Company focus is on recycling and co-processing of waste. Some of the initiatives on waste management are:
- Plastic waste is mainly disposed through co-processing by the Company and a very small quantity like burst bags through authorised scrap dealers
- Bio-medical waste is disposed through incineration at authorised Common Biomedical Waste Treatment Facilities
- E-waste is recycled through authorised recyclers
- Hazardous waste (used oil) is reused at plant or is co-processed in cement kiln and the quantity which cannot be co-processed is sent to common authorised facility
- Scrap is sold to authorised vendors
- Mining overburden is repurposed and used for backfilling within the mines
- Fly-ash is used in manufacturing of blended cement.
- Discarded drums are sent to authorised recyclers
Waste Disposal
The Company focus is on recycling of waste. Only biomedical waste is sent to common facility for incineration. There is no disposal of hazardous wastes in landfills.
Hazardous Waste sent to Landfill
Circular Economy
During the year, ACC utilised 12 million tonnes of waste-derived resources, The wastes are used as resources in two ways:- one is alternate fuels where wastes like plastic waste, municipal wastes, agri wastes are used for replacing fossil fuels. Another way is where wastes like fly-ash, slag, gypsum waste, etc. are used to replace use of mined resources.
of Waste-derived Resources Utilised during the Year

Biodiversity Management
Biodiversity management is a key priority in the Company's materiality assessment, recognising the vital role of healthy ecosystems in mitigating natural disasters. Robust biodiversity supports essential ecological services critical to both business and society. ACC’s comprehensive biodiversity policy addresses operational impacts by guiding the identification and assessment of biodiversity-related risks across project sites. It implements a structured mitigation hierarchy — avoid, minimise, restore, and offset — while ensuring regular progress evaluation. The policy applies to all operations, suppliers, and value chain partners, reinforcing the Company's commitment to sustainable environmental practices. It aims to achieve No Net Deforestation through time-bound afforestation programmes and No Net Loss of Biodiversity across all operations and sites with critical habitats. Ultimately, the objective is to achieve a Net Positive Gain in biodiversity, strengthening the natural environment for future generations.
ACC has conducted a detailed Nature Risk Assessment, including a Biodiversity Risk Assessment, based on the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) LEAP approach in 10 km radius across its plants and mines. This methodology facilitated the identification, evaluation, and reporting of nature-related dependencies and impacts. The TNFD defines dependencies as ecosystem services essential for business operations, such as a clean and reliable water supply.

At the same time, businesses impact environmental assets and ecosystem services, which may have either positive or negative consequences. These impacts, in turn, create risks due to organisational dependencies on nature.
Nature-related risks can be physical, arising from climatic events (e.g. extreme weather) or geological changes (e.g. seismic activity), which may be acute, chronic, or both. They can also be transition risks, resulting from misalignment between an organisation’s strategy and the evolving regulatory and policy landscape. On the other hand, nature-related opportunities involve activities that create positive outcomes by reducing environmental impact or contributing to ecosystem restoration. is highly dependent on natural capital, particularly abiotic services such as minerals (e.g. limestone) and water. Indirectly, the business relies on ecosystem regulation services, including climate and water regulation, as well as protection against floods and storms, which are crucial for operational continuity.
However, also has significant impacts on natural capital, particularly through mining operations. Extracting raw materials requires removing layers of the earth’s crust, leading to land-use changes that affect local flora and fauna. ACC remains committed to mitigating these impacts through responsible resource management and sustainable practices.
Biodiversity Risk Assessment
The operations were assessed within a 10 km radius, with the operational site as the central point, to evaluate potential impacts and dependencies on local biodiversity and ecosystem services. The IBBI Ecosystem Services Matrix tool was utilised for ecosystem and service mapping, while risk identification was aligned with the International Finance Corporation Performance Standard 6, the UN CBD’s Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework, DJSI, and the TNFD Framework. Additional tools such as DOPA, eBird India, and Global Mangrove Watch were also employed.
Following the assessment, a risk categorisation matrix was developed for each site, evaluating both impact and dependency. The findings identified high-risk, medium-risk, and low-risk sites requiring targeted action to mitigate biodiversity impacts.
Biodiversity Action Plan
To mitigate the biodiversity risks identified in its assessment, ACC has developed a comprehensive Biodiversity Action Plan (BAP) that integrates nature-based solutions and aligns with the IUCN Mitigation Hierarchy. The BAP includes site-specific action plans, encompassing initiatives such as greenbelt development, wildlife monitoring in and around the plant, the creation of rainwater harvesting structures, and a mangrove restoration plan, among others.
Biodiversity Mitigation Hierarchy
| Avoid | Reduce | Regenerate & Restore | Transform |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implementing measures to prevent adverse impacts on biodiversity from the outset. | Reducing unavoidable improved management impacts through practices and technologies. | Rehabilitating affected ecosystems to restore their functions and services. | Actions to achieve No Net Deforestation and No Net loss to Biodiversity and progress towards Net Positive. |
| E.g. Greenbelt Management: Adhering to CPCB guidelines by using native tree species and avoiding monoculture plantations to enhance biodiversity and mitigate pollution. |
E.g. Lighting
Management: Re-orienting
lighting systems to
reduce impacts on
nocturnal wildlife.
E.g. Compensatory tree plantations in case of trees cut during expansion. |
E.g. Rainwater Harvesting: Developing structures to increase groundwater recharge and restore local water bodies; Mangrove Restoration. | E.g. Targets to plant trees at each site and working with communities around. |
Biodiversity Protection and Enhancement Measures
ACC strictly adheres to Indian laws and regulations, including the Forest Conservation Act and the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA) Act, ensuring compliance with the principle of No Net Deforestation. Under the Forest Conservation Act (1980) and the Compensatory Fund Act (2016), the Company is required to compensate for any forest land cleared for operational activities through afforestation. Additionally, ACC has a Mine Closure Plan in place at all mining locations, which includes compensatory afforestation and rehabilitation measures upon closure. The Company also complies with the Green Belt Development guidelines set by the Government of India. Other initiatives to prevent environmental degradation and enhance biodiversity include:

Community Collaboration
ACC works closely with local communities to manage the planted and rehabilitated areas effectively, and partners with them to manage any adjoining offset areas with initiatives in adjoining area.
Tree Plantation Targets
ACC as part of Adani portfolio of companies is committed to grow 5.9 million trees by 2030. Out of this, 5.1 million trees are already grown.
Enhancing Degraded Habitats
The Company implemented targeted habitat management plans to regenerate and restore degraded habitats across our sites.
Mining Overburden Management
Mining overburden is stored separately in non-mineralised zones as per the approved mine plan and used for mine rehabilitation. Progressive mine closure plans are available as per statute for all locations.
Daytime Operations
ACC restricts mining operations and raw material transportation to daylight hours when operating near protected areas to minimise disturbance.
Capacity and Awareness Building
ACC priorities continuous training for its team members who work closely with local communities, ensuring its activities have minimal biodiversity impact. Awareness programmes are regularly held for all stakeholders.

IBBI Membershi
ACC is a member of India Business and Biodiversity Initiative (IBBI). IBBI serves as a national platform of businesses and its stakeholders for dialogue sharing and learning, ultimately leading to mainstreaming sustainable management of biological diversity into businesses.
Greening Initiatives at ACC’s Gagal Plant
In order to improve biodiversity, ACC has made significant investments towards greening efforts across various areas near its Gagal Plant, including non-mine zones, closed mine sites, manufacturing facilities and integrated townships. These initiatives have transformed the Gagal plant into one of the greenest areas in Bilaspur, Himachal Pradesh, attracting visitors with its scenic beauty. The Gagal plant began operations in 1984 at Barmana Hill, and after mining concluded there in the 1990's, activities shifted to Gagal Hill. The rehabilitation of the Barmana mine into a mango orchard has further added to its appeal for visitors.
The Gagal plant’s mining lease covers 231.25 hectares, with 58 hectares allocated to active mining. The remaining land was previously barren but has since been transformed into a dense forest through artificial regeneration using local species. Over nearly two decades, the area was developed, and the plant has maintained it for over four decades. The hilly landscape is home to different species, acting as a habitat for leopards, monitor lizards, geckos and different types of birds. Till date, over 1 million trees have been planted across 202.5 hectares in and around the plant, mines, township and community areas. Animals such as langurs, macaques and Bengal monitor lizards have adapted to the ecosystem.
Key factors in the project’s success include local community involvement, employment opportunities, and collaboration with the local forest department. Challenges, such as illegal felling and forest fires, were addressed through community participation and innovative solutions like co-processing pine needles in cement kilns. The initiative has improved biodiversity, controlled soil erosion and enhanced water levels, contributing to the area's ecological balance. Moving forward, ACC plans to plant over 2,000 saplings annually and expand efforts to community areas.

Responsible Mining
ACC acknowledges the vital role of mining in its production process while remaining deeply conscious of its environmental impact. As a responsible corporate entity, the Company is committed to sustainable mining practices that prioritise environmental conservation, biodiversity protection, and social responsibility. Ensuring full compliance with all relevant laws and regulations, ACC integrates sustainability into its operations with a comprehensive Mine Closure Plan, incorporating compensatory afforestation and rehabilitation.
To minimise environmental impact, all mines utilise controlled blasting with high-precision electronic detonators, enhancing safety and reducing emissions. Scientific mining technologies aid mineral conservation, while dust suppression measures during drilling and well-maintained haul roads help curb airborne pollutants. In select locations, limestone is transported via covered tippers to prevent dust and spillage.
ACC enforces stringent health and safety standards and actively fosters biodiversity by developing green belts around mines and plants. Overburden is responsibly managed, transforming some sites into thriving habitats for migratory and local birds. Additionally, water conservation efforts, including groundwater recharge through closed mine pits, further reinforce ACC’s commitment to responsible and sustainable mining.

Regulatory Compliance
ACC understands that regulatory compliance is fundamental to responsible and sustainable operations. The Company rigorously adheres to a comprehensive framework of environmental regulations, ensuring all necessary approvals are secured. To maintain transparency and accountability, compliance is meticulously monitored through the Legatrix software. Key environmental regulations governing its operations include:
- Environmental Clearances
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974
- The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981
- Noise Pollution (Regulation and Control) Rules, 2000
- The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
- Hazardous and other Wastes (Management & Transboundary Movement) Rules, 2016
- Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016
- Bio Medical Waste Rules, 2016
- Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016
- E-Waste Rules, 2016
- The Construction and Demolition Waste Management Rules, 2016
ACC goes above and beyond compliance, setting new industry benchmarks through its focus on sustainability and environmental stewardship. The Company takes a proactive approach to environmental management, constantly innovating and refining its practices to drive meaningful, lasting impact.